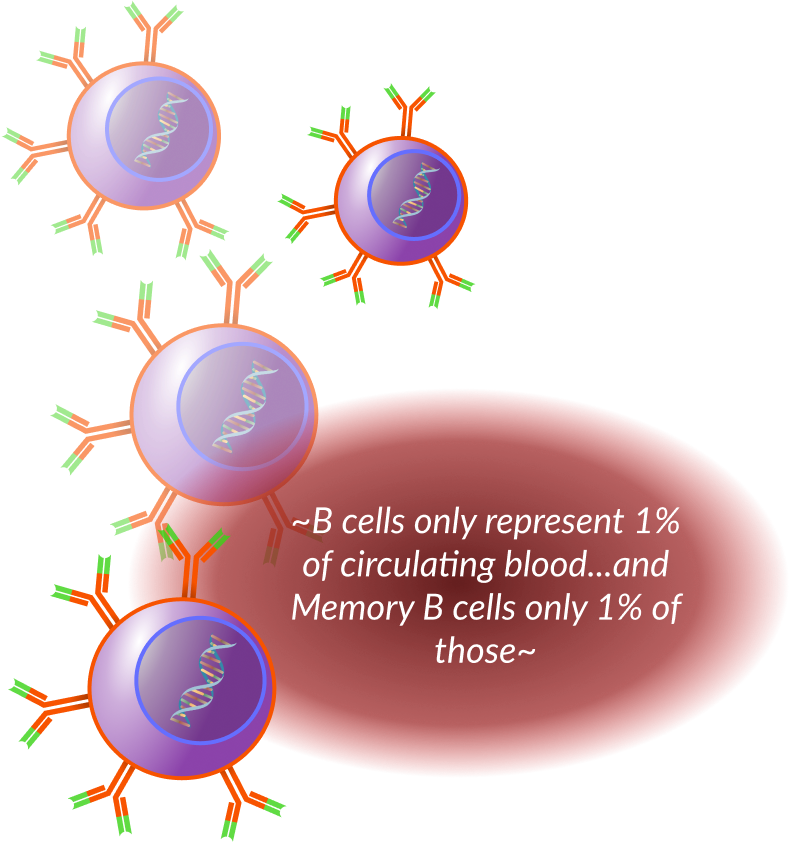
History of Antibody Discovery
Since the 70s, scientists have progressively attempted to recreate
the human immune system’s most powerful disease fighting mechanism: first
through animal and chimeric hybridization and then humanized and recombinant
forms.
All of these methods had shortcomings through immune system rejection,
toxicity, prohibitive costs, or limited antibody diversity.






1978